id: 10141
lecture: Offspring phenotypes: dominant or recessive? How do you determine an organism's phenotype for a trait? Look at the combination of alleles in the organism's genotype for the gene that affects that trait. Some alleles have types called dominant and recessive. These two types can cause different versions of the trait to appear as the organism's phenotype. If an organism's genotype has at least one dominant allele for a gene, the organism's phenotype will be the dominant allele's version of the gene's trait. If an organism's genotype has only recessive alleles for a gene, the organism's phenotype will be the recessive allele's version of the gene's trait. A Punnett square shows what types of offspring a cross can produce. The expected ratio of offspring types compares how often the cross produces each type of offspring, on average. To write this ratio, count the number of boxes in the Punnett square representing each type. For example, consider the Punnett square below. | F | f F | FF | Ff f | Ff | ff There is 1 box with the genotype FF and 2 boxes with the genotype Ff. So, the expected ratio of offspring with the genotype FF to those with Ff is 1:2.
question: What is the expected ratio of offspring with sweet fruit to offspring with sour fruit? Choose the most likely ratio.
choice: (A) 4:0 (B) 0:4 (C) 3:1 (D) 2:2 (E) 1:3
context: In a group of muskmelon plants, some individuals have sour fruit and others have sweet fruit. In this group, the gene for the fruit taste trait has two alleles. The allele for sour fruit (F) is dominant over the allele for sweet fruit (f). This Punnett square shows a cross between two muskmelon plants.
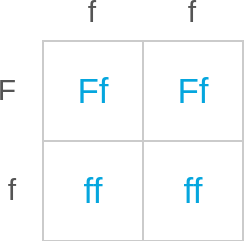
answer: D
rationale: Offspring phenotypes: dominant or recessive? How do you determine an organism's phenotype for a trait? Look at the combination of alleles in the organism's genotype for the gene that affects that trait. Some alleles have types called dominant and recessive. These two types can cause different versions of the trait to appear as the organism's phenotype. If an organism's genotype has at least one dominant allele for a gene, the organism's phenotype will be the dominant allele's version of the gene's trait. If an organism's genotype has only recessive alleles for a gene, the organism's phenotype will be the recessive allele's version of the gene's trait. A Punnett square shows what types of offspring a cross can produce. The expected ratio of offspring types compares how often the cross produces each type of offspring, on average. To write this ratio, count the number of boxes in the Punnett square representing each type. For example, consider the Punnett square below. | F | f F | FF | Ff f | Ff | ff There is 1 box with the genotype FF and 2 boxes with the genotype Ff. So, the expected ratio of offspring with the genotype FF to those with Ff is 1:2. To determine how many boxes in the Punnett square represent offspring with sweet fruit or sour fruit, consider whether each phenotype is the dominant or recessive allele's version of the fruit taste trait. The question tells you that the F allele, which is for sour fruit, is dominant over the f allele, which is for sweet fruit. Sweet fruit is the recessive allele's version of the fruit taste trait. A muskmelon plant with the recessive version of the fruit taste trait must have only recessive alleles for the fruit taste gene. So, offspring with sweet fruit must have the genotype ff. There are 0 boxes in the Punnett square with the genotype ff. Sour fruit is the dominant allele's version of the fruit taste trait. A muskmelon plant with the dominant version of the fruit taste trait must have at least one dominant allele for the fruit taste gene. So, offspring with sour fruit must have the genotype FF or Ff. All 4 boxes in the Punnett square have the genotype FF or Ff. So, the expected ratio of offspring with sweet fruit to offspring with sour fruit is 0:4. This means that, based on the Punnett square, this cross will never produce offspring with sweet fruit. Instead, this cross is expected to always produce offspring with sour fruit. The answer is B.
generated_skill:
solution: To determine how many boxes in the Punnett square represent offspring with sweet fruit or sour fruit, consider whether each phenotype is the dominant or recessive allele's version of the fruit taste trait. The question tells you that the F allele, which is for sour fruit, is dominant over the f allele, which is for sweet fruit. Sweet fruit is the recessive allele's version of the fruit taste trait. A muskmelon plant with the recessive version of the fruit taste trait must have only recessive alleles for the fruit taste gene. So, offspring with sweet fruit must have the genotype ff. There are 2 boxes in the Punnett square with the genotype ff. These boxes are highlighted below. Sour fruit is the dominant allele's version of the fruit taste trait. A muskmelon plant with the dominant version of the fruit taste trait must have at least one dominant allele for the fruit taste gene. So, offspring with sour fruit must have the genotype FF or Ff. There are 2 boxes in the Punnett square with the genotype FF or Ff. These boxes are highlighted below. So, the expected ratio of offspring with sweet fruit to offspring with sour fruit is 2:2. This means that, on average, this cross will produce 2 offspring with sweet fruit for every 2 offspring with sour fruit.
skill: Use Punnett squares to calculate ratios of offspring types
id: 11073
lecture: An object has different properties. A property of an object can tell you how it looks, feels, tastes, or smells. Properties can also tell you how an object will behave when something happens to it. Different objects can have properties in common. You can use these properties to put objects into groups. Grouping objects by their properties is called classification.
question: Which property do these three objects have in common?
choice: (A) translucent (B) transparent (C) sour
context: Select the best answer.
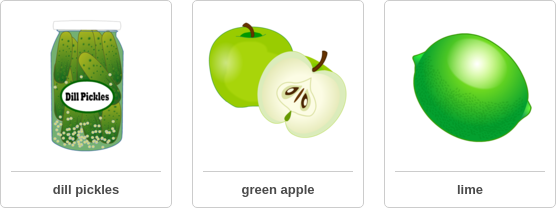
answer: C
rationale: An object has different properties. A property of an object can tell you how it looks, feels, tastes, or smells. Properties can also tell you how an object will behave when something happens to it. Different objects can have properties in common. You can use these properties to put objects into groups. Grouping objects by their properties is called classification. Look at each object. For each object, decide if it has that property. A lemon has a sour taste. The ocean water and the green apple are not sour. You can see clearly through a transparent object. The ocean water is transparent, but the green apple and the carrot are not. A translucent object lets light through. But you cannot see clearly through a translucent object. All three objects are translucent. The property that all three objects have in common is translucent. The answer is A.
generated_skill:
solution: Look at each object. For each object, decide if it has that property. A translucent object lets light through. But you cannot see clearly through a translucent object. The green apple is not translucent. You can see clearly through a transparent object. The green apple and the lime are not transparent. A lemon has a sour taste. All three objects are sour. The property that all three objects have in common is sour.
skill: Compare properties of objects
id: 11757
lecture: Magnets can pull or push on each other without touching. When magnets attract, they pull together. When magnets repel, they push apart. These pulls and pushes between magnets are called magnetic forces. The stronger the magnetic force between two magnets, the more strongly the magnets attract or repel each other. You can change the strength of a magnetic force between two magnets by changing the distance between them. The magnetic force is stronger when the magnets are closer together.
question: Think about the magnetic force between the magnets in each pair. Which of the following statements is true?
choice: (A) The magnetic force is stronger in Pair 2. (B) The magnetic force is stronger in Pair 1. (C) The strength of the magnetic force is the same in both pairs.
context: The images below show two pairs of magnets. The magnets in different pairs do not affect each other. All the magnets shown are made of the same material.
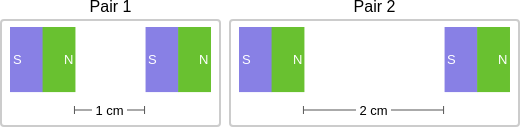
answer: B
rationale: Magnets can pull or push on each other without touching. When magnets attract, they pull together. When magnets repel, they push apart. These pulls and pushes between magnets are called magnetic forces. The stronger the magnetic force between two magnets, the more strongly the magnets attract or repel each other. You can change the strength of a magnetic force between two magnets by changing the distance between them. The magnetic force is stronger when the magnets are closer together. Distance affects the strength of the magnetic force. When magnets are closer together, the magnetic force between them is stronger. The magnets in Pair 2 are closer together than the magnets in Pair 1. So, the magnetic force is stronger in Pair 2 than in Pair 1. The answer is A.
generated_skill:
solution: Distance affects the strength of the magnetic force. When magnets are closer together, the magnetic force between them is stronger. The magnets in Pair 1 are closer together than the magnets in Pair 2. So, the magnetic force is stronger in Pair 1 than in Pair 2.
skill: Compare strengths of magnetic forces
id: 12072
lecture: A solution is made up of two or more substances that are completely mixed. In a solution, solute particles are mixed into a solvent. The solute cannot be separated from the solvent by a filter. For example, if you stir a spoonful of salt into a cup of water, the salt will mix into the water to make a saltwater solution. In this case, the salt is the solute. The water is the solvent. The concentration of a solute in a solution is a measure of the ratio of solute to solvent. Concentration can be described in terms of particles of solute per volume of solvent. concentration = particles of solute / volume of solvent
question: Which solution has a higher concentration of yellow particles?
choice: (A) Solution A (B) neither; their concentrations are the same (C) Solution B
context: The diagram below is a model of two solutions. Each yellow ball represents one particle of solute.
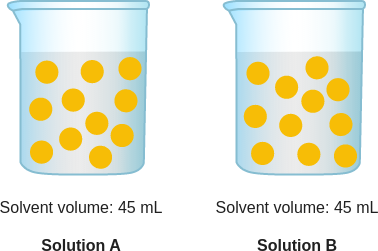
answer: B
rationale: A solution is made up of two or more substances that are completely mixed. In a solution, solute particles are mixed into a solvent. The solute cannot be separated from the solvent by a filter. For example, if you stir a spoonful of salt into a cup of water, the salt will mix into the water to make a saltwater solution. In this case, the salt is the solute. The water is the solvent. The concentration of a solute in a solution is a measure of the ratio of solute to solvent. Concentration can be described in terms of particles of solute per volume of solvent. concentration = particles of solute / volume of solvent In Solution A and Solution B, the yellow particles represent the solute. To figure out which solution has a higher concentration of yellow particles, look at both the number of yellow particles and the volume of the solvent in each container. Use the concentration formula to find the number of yellow particles per milliliter. Solution B has more yellow particles per milliliter. So, Solution B has a higher concentration of yellow particles. The answer is C.
generated_skill:
solution: In Solution A and Solution B, the yellow particles represent the solute. To figure out which solution has a higher concentration of yellow particles, look at both the number of yellow particles and the volume of the solvent in each container. Use the concentration formula to find the number of yellow particles per milliliter. Solution A and Solution B have the same number of yellow particles per milliliter. So, their concentrations are the same.
skill: Compare concentrations of solutions
id: 12397
lecture:
question: Which country is highlighted?
choice: (A) Haiti (B) the Dominican Republic (C) Cuba (D) The Bahamas
context: N/A
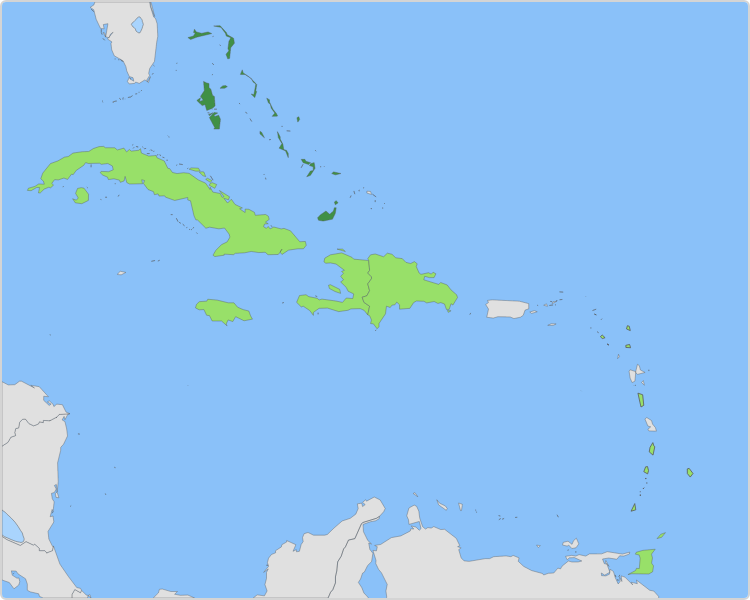
answer: D
rationale: This country is the Dominican Republic. Why does the Dominican Republic share its island with another country? The Dominican Republic and Haiti share the island of Hispaniola. It is home to the earliest European settlements in the Americas. Christopher Columbus founded the first European settlement on the island in 1492 during his first voyage across the Atlantic. Though many people lived on the island before Columbus's arrival, European countries quickly began to colonize the island. Eventually France and Spain both established colonies. The Spanish colony eventually became the country of the Dominican Republic, and the French colony eventually became the country of Haiti. Today, people in the two countries speak different languages and have many cultural differences. The answer is B.
generated_skill:
solution: This country is The Bahamas.
skill: Identify and select countries of the Caribbean
id: 12418
lecture: Magnets can pull or push on each other without touching. When magnets attract, they pull together. When magnets repel, they push apart. These pulls and pushes between magnets are called magnetic forces. The strength of a force is called its magnitude. The greater the magnitude of the magnetic force between two magnets, the more strongly the magnets attract or repel each other. You can change the magnitude of a magnetic force between two magnets by changing the distance between them. The magnitude of the magnetic force is greater when there is a smaller distance between the magnets.
question: Think about the magnetic force between the magnets in each pair. Which of the following statements is true?
choice: (A) The magnitude of the magnetic force is the same in both pairs. (B) The magnitude of the magnetic force is greater in Pair 2. (C) The magnitude of the magnetic force is greater in Pair 1.
context: The images below show two pairs of magnets. The magnets in different pairs do not affect each other. All the magnets shown are made of the same material.

answer: B
rationale: Magnets can pull or push on each other without touching. When magnets attract, they pull together. When magnets repel, they push apart. These pulls and pushes between magnets are called magnetic forces. The strength of a force is called its magnitude. The greater the magnitude of the magnetic force between two magnets, the more strongly the magnets attract or repel each other. You can change the magnitude of a magnetic force between two magnets by changing the distance between them. The magnitude of the magnetic force is greater when there is a smaller distance between the magnets. The magnets in Pair 2 attract. The magnets in Pair 1 repel. But whether the magnets attract or repel affects only the direction of the magnetic force. It does not affect the magnitude of the magnetic force. Distance affects the magnitude of the magnetic force. When there is a smaller distance between magnets, the magnitude of the magnetic force between them is greater. There is a smaller distance between the magnets in Pair 1 than in Pair 2. So, the magnitude of the magnetic force is greater in Pair 1 than in Pair 2. The answer is C.
generated_skill:
solution: Distance affects the magnitude of the magnetic force. When there is a smaller distance between magnets, the magnitude of the magnetic force between them is greater. There is a smaller distance between the magnets in Pair 2 than in Pair 1. So, the magnitude of the magnetic force is greater in Pair 2 than in Pair 1.
skill: Compare magnitudes of magnetic forces
id: 12577
lecture: A force is a push or a pull that one object applies to another. Every force has a direction. The direction of a push is away from the object that is pushing. The direction of a pull is toward the object that is pulling.
question: What is the direction of this pull?
choice: (A) away from the magnet (B) toward the magnet
context: A horseshoe magnet attracts paper clips with a magnetic force. This magnetic force pulls the paper clips upward so they do not fall.

answer: B
rationale: Magnets can pull or push on each other without touching. When magnets attract, they pull together. When magnets repel, they push apart. The direction of a pull or push is away from the magnet that is attracting or repelling. The paper clips are attracted to the horseshoe magnet. So, the pull is away from the magnet. The answer is A.
generated_skill:
solution: The magnet pulls the paper clips upward. The direction of the pull is toward the magnet.
skill: Identify directions of forces
id: 12611
lecture:
question: Which of these cities is marked on the map?
choice: (A) Los Angeles (B) Chicago (C) San Francisco (D) Denver
context: N/A
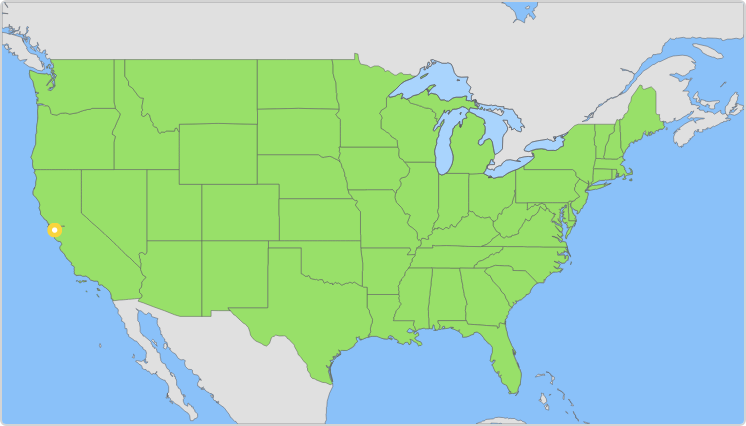
answer: C
rationale: The city is Denver, Colorado. Los Angeles, Chicago, and San Francisco are marked with gray circles on the map below. The answer is D.
generated_skill:
solution: The city is San Francisco, California. Los Angeles, Denver, and Chicago are marked with gray circles on the map below.
skill: Major U.S. cities
id: 12645
lecture: An object has different properties. A property of an object can tell you how it looks, feels, tastes, or smells. Properties can also tell you how an object will behave when something happens to it. Different objects can have properties in common. You can use these properties to put objects into groups. Grouping objects by their properties is called classification.
question: Which property do these three objects have in common?
choice: (A) fragile (B) sticky (C) colorful
context: Select the best answer.

answer: C
rationale: An object has different properties. A property of an object can tell you how it looks, feels, tastes, or smells. Properties can also tell you how an object will behave when something happens to it. Different objects can have properties in common. You can use these properties to put objects into groups. Grouping objects by their properties is called classification. Look at each object. For each object, decide if it has that property. A sticky object can attach or stick to other things. All three objects are sticky. A colorful object has one or more bright colors. The socks are colorful, but the masking tape and the paint are not. A fragile object will break into pieces if you drop it. None of the objects are fragile. The property that all three objects have in common is sticky. The answer is B.
generated_skill:
solution: Look at each object. For each object, decide if it has that property. A colorful object has one or more bright colors. All three objects are colorful. A sticky object can attach or stick to other things. None of the objects are sticky. A fragile object will break into pieces if you drop it. The socks and the hot air balloon are not fragile. The property that all three objects have in common is colorful.
skill: Compare properties of objects
id: 13162
lecture: Magnets can pull or push on each other without touching. When magnets attract, they pull together. When magnets repel, they push apart. These pulls and pushes between magnets are called magnetic forces. The strength of a force is called its magnitude. The greater the magnitude of the magnetic force between two magnets, the more strongly the magnets attract or repel each other. You can change the magnitude of a magnetic force between two magnets by changing the distance between them. The magnitude of the magnetic force is smaller when there is a greater distance between the magnets.
question: Think about the magnetic force between the magnets in each pair. Which of the following statements is true?
choice: (A) The magnitude of the magnetic force is smaller in Pair 1. (B) The magnitude of the magnetic force is smaller in Pair 2. (C) The magnitude of the magnetic force is the same in both pairs.
context: The images below show two pairs of magnets. The magnets in different pairs do not affect each other. All the magnets shown are made of the same material, but some of them are different shapes.
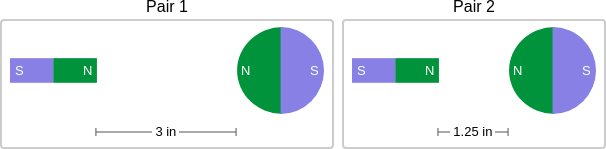
answer: A
rationale: Magnets can pull or push on each other without touching. When magnets attract, they pull together. When magnets repel, they push apart. These pulls and pushes between magnets are called magnetic forces. The strength of a force is called its magnitude. The greater the magnitude of the magnetic force between two magnets, the more strongly the magnets attract or repel each other. You can change the magnitude of a magnetic force between two magnets by changing the distance between them. The magnitude of the magnetic force is smaller when there is a greater distance between the magnets. The magnets in Pair 1 attract. The magnets in Pair 2 repel. But whether the magnets attract or repel affects only the direction of the magnetic force. It does not affect the magnitude of the magnetic force. Distance affects the magnitude of the magnetic force. When there is a greater distance between magnets, the magnitude of the magnetic force between them is smaller. There is a greater distance between the magnets in Pair 2 than in Pair 1. So, the magnitude of the magnetic force is smaller in Pair 2 than in Pair 1. The answer is B.
generated_skill:
solution: Distance affects the magnitude of the magnetic force. When there is a greater distance between magnets, the magnitude of the magnetic force between them is smaller. There is a greater distance between the magnets in Pair 1 than in Pair 2. So, the magnitude of the magnetic force is smaller in Pair 1 than in Pair 2.
skill: Compare magnitudes of magnetic forces