id: 8295
question: Think about the magnetic force between the magnets in each pair. Which of the following statements is true?
choice: (A) The magnetic force is stronger in Pair 1. (B) The strength of the magnetic force is the same in both pairs. (C) The magnetic force is stronger in Pair 2.
context: The images below show two pairs of magnets. The magnets in different pairs do not affect each other. All the magnets shown are made of the same material.
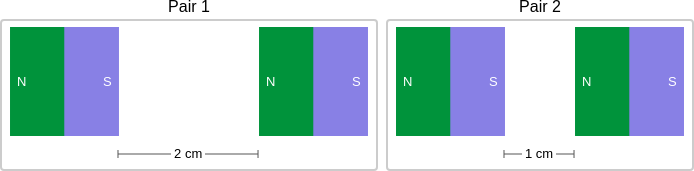
gold answer: C
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: Magnets can pull or push on each other without touching.
- 1: When magnets attract, they pull together.
- 2: When magnets repel, they push apart.
- 3: These pulls and pushes between magnets are called magnetic forces.
- 4: The stronger the magnetic force between two magnets, the more strongly the magnets attract or repel each other.
- 5: You can change the strength of a magnetic force between two magnets by changing the distance between them.
- 6: The magnetic force is stronger when the magnets are closer together.
- 7: Distance affects the strength of the magnetic force.
- 8: When magnets are closer together, the magnetic force between them is stronger.
- 9: The magnets in Pair 1 are closer together than the magnets in Pair 2.
- 10: So, the magnetic force is stronger in Pair 1 than in Pair 2.
- 11: The answer is A.
id: 8303
question: Based on the text, how does a sloth's fur help protect it?
choice: (A) A sloth's fur helps it dry off quickly. (B) A sloth's fur protects its important organs. (C) A sloth's fur helps it cling to tree branches.
context: Read the text about sloths. Sloths are known for being one of the slowest animals on the planet. They also sleep up to twenty hours every day. Even though sloths are lethargic, they manage to stay safe by living in the treetops of South and Central America. Sloths have special qualities that help them spend their lives hanging from branches. For example, sloths' long fur grows in the opposite direction from that of most animals. Most animals' fur grows downward, which helps rainwater run down off the animal. Sloths' fur, however, grows upward. When a sloth is hanging upside down, rainwater is still directed off its body. This helps the sloth dry off more quickly. Sloth fur has another special purpose. Each strand of fur has grooves that collect algae. The algae give the sloth a greenish color, which helps it blend in with its leafy environment. Along with sloths' slow movement, this disguise makes sloths hard for predators to spot. Sloths also have long, curved claws on their front and back legs. Sloths can use their claws to protect themselves from predators. More importantly, the long, sharp claws curve around branches for a powerful grip. In this way, sloths' claws keep them from slipping and falling out of trees. Hanging upside down all day can be hard for other reasons. In most animals, hanging would cause the stomach, heart, and other organs to press on the lungs. Not for sloths, though. Sloths have special bands of tissue called adhesions that help attach certain organs to the rib cage. These bands of tissue hold the organs in place so they don't press down on the sloth's lungs. Thus the sloth stays healthy and comfortable while hanging in its upside-down world.

gold answer: A
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: Look at the text in bold below.
- 1: It tells you two ways a sloth's fur helps protect it.
- 2: For example, sloths' long fur grows in the opposite direction from that of most animals.
- 3: Most animals' fur grows downward, which helps rainwater run down off the animal.
- 4: Sloths' fur, however, grows upward.
- 5: When a sloth is hanging upside down, rainwater is still directed off its body.
- 6: This helps the sloth dry off more quickly.
- 7: Sloth fur has another special purpose.
- 8: Each strand of fur has grooves that collect algae.
- 9: The algae give the sloth a greenish color, which helps it blend in with its leafy environment.
- 10: Along with sloths' slow movement, this disguise makes sloths hard for predators to spot.
- 11: The answer is C.
id: 8318
question: Compare the average kinetic energies of the particles in each sample. Which sample has the higher temperature?
choice: (A) sample A (B) sample B (C) neither; the samples have the same temperature
context: The diagrams below show two pure samples of gas in identical closed, rigid containers. Each colored ball represents one gas particle. Both samples have the same number of particles.
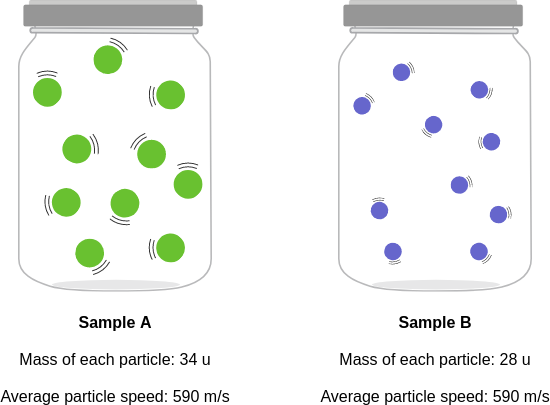
gold answer: A
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: The temperature of a substance depends on the average kinetic energy of the particles in the substance.
- 1: The higher the average kinetic energy of the particles, the higher the temperature of the substance.
- 2: The kinetic energy of a particle is determined by its mass and speed.
- 3: For a pure substance, the greater the mass of each particle in the substance and the higher the average speed of the particles, the higher their average kinetic energy.
- 4: Each particle in sample B has more mass than each particle in sample A.
- 5: The particles in sample B also have a higher average speed than the particles in sample A.
- 6: So, the particles in sample B have a higher average kinetic energy than the particles in sample A.
- 7: Because the particles in sample B have the higher average kinetic energy, sample B must have the higher temperature.
- 8: The answer is B.
id: 8419
question: Would you find the word blot on a dictionary page with the following guide words? beef - bolt
choice: (A) yes (B) no
gold answer: A
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: Guide words appear on each page of a dictionary.
- 1: They tell you the first word and last word on the page.
- 2: The other words on the page come between the guide words in alphabetical order.
- 3: To put words in alphabetical order, put them in order by their first letters.
- 4: If the first letters are the same, look at the second letters.
- 5: If the second letters are the same, look at the third letters, and so on.
- 6: If one word is shorter, and there are no more letters to compare, then the shorter word comes first in alphabetical order.
- 7: For example, be comes before bed.
- 8: Put the words in alphabetical order.
- 9: Since blot is not between the guide words beef - bolt, it would not be found on that page.
- 10: The answer is B.
id: 8513
question: Compare the average kinetic energies of the particles in each sample. Which sample has the higher temperature?
choice: (A) neither; the samples have the same temperature (B) sample A (C) sample B
context: The diagrams below show two pure samples of gas in identical closed, rigid containers. Each colored ball represents one gas particle. Both samples have the same number of particles.
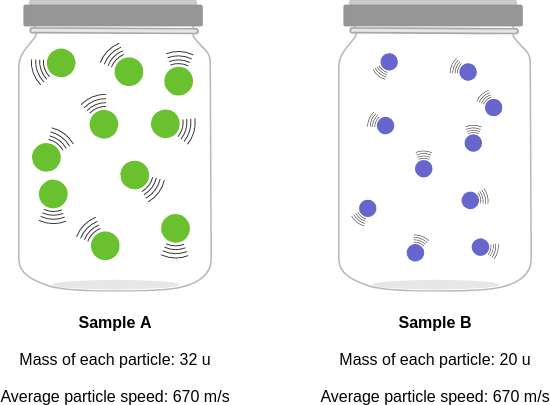
gold answer: B
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: The temperature of a substance depends on the average kinetic energy of the particles in the substance.
- 1: The higher the average kinetic energy of the particles, the higher the temperature of the substance.
- 2: The kinetic energy of a particle is determined by its mass and speed.
- 3: For a pure substance, the greater the mass of each particle in the substance and the higher the average speed of the particles, the higher their average kinetic energy.
- 4: Each particle in sample B has more mass than each particle in sample A.
- 5: The particles in sample B also have a higher average speed than the particles in sample A.
- 6: So, the particles in sample B have a higher average kinetic energy than the particles in sample A.
- 7: Because the particles in sample B have the higher average kinetic energy, sample B must have the higher temperature.
- 8: The answer is C.
id: 8635
question: Think about the magnetic force between the magnets in each pair. Which of the following statements is true?
choice: (A) The magnitude of the magnetic force is greater in Pair 2. (B) The magnitude of the magnetic force is greater in Pair 1. (C) The magnitude of the magnetic force is the same in both pairs.
context: The images below show two pairs of magnets. The magnets in different pairs do not affect each other. All the magnets shown are made of the same material, but some of them are different shapes.
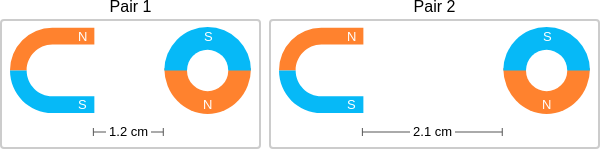
gold answer: B
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: Magnets can pull or push on each other without touching.
- 1: When magnets attract, they pull together.
- 2: When magnets repel, they push apart.
- 3: These pulls and pushes between magnets are called magnetic forces.
- 4: The strength of a force is called its magnitude.
- 5: The greater the magnitude of the magnetic force between two magnets, the more strongly the magnets attract or repel each other.
- 6: You can change the magnitude of a magnetic force between two magnets by changing the distance between them.
- 7: The magnitude of the magnetic force is greater when there is a smaller distance between the magnets.
- 8: Distance affects the magnitude of the magnetic force.
- 9: When there is a smaller distance between magnets, the magnitude of the magnetic force between them is greater.
- 10: There is a smaller distance between the magnets in Pair 2 than in Pair 1.
- 11: So, the magnitude of the magnetic force is greater in Pair 2 than in Pair 1.
- 12: The answer is A.
id: 8758
question: Based on this information, what is this plant's phenotype for the thorns trait?
choice: (A) having thorns (B) not having thorns
context: In a group of rose plants, some individuals have thorns and others do not. In this group, the gene for the thorns trait has two alleles. The allele for having thorns (R) is dominant over the allele for not having thorns (r). A certain rose plant from this group has the heterozygous genotype Rr for the thorns gene.
gold answer: A
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: All organisms have pieces of hereditary material called genes, which are passed from parents to offspring.
- 1: Genes contain instructions for building the parts of an organism.
- 2: An organism's genes affect its observable traits, including its appearance, its behavior, and which diseases it may have.
- 3: Genes may have different alleles, or forms, that can cause different versions of a trait.
- 4: For example, flower color is a trait in pea plants.
- 5: The gene for this trait has two possible alleles.
- 6: Each allele is represented by an uppercase or lowercase letter.
- 7: The allele F is for purple flowers, and the allele f is for white flowers.
- 8: Each pea plant has two alleles for the flower color gene—one allele inherited from each parent.
- 9: An organism's genotype for a gene is its combination of alleles for that gene.
- 10: So, a pea plant may have a genotype of FF, Ff, or ff for the flower color gene.
- 11: An organism's phenotype for a trait is its observable version of that trait, which depends on the organism's combination of alleles.
- 12: A pea plant may have a phenotype of purple flowers or white flowers for the flower color trait.
- 13: Some traits, like flower color in pea plants, are controlled by a single gene.
- 14: Most plants and animals have a genotype made up of two alleles for these traits.
- 15: These two alleles determine whether an organism is homozygous or heterozygous for the gene.
- 16: An organism with two identical alleles for a gene is homozygous for that gene.
- 17: A pea plant with the genotype FF or ff is homozygous for the flower color gene.
- 18: An organism with two different alleles for a gene is heterozygous for that gene.
- 19: A pea plant with the genotype Ff is heterozygous for the flower color gene.
- 20: The types of alleles in an organism's genotype determine the organism's phenotype.
- 21: Some alleles have types called dominant and recessive.
- 22: These two types can cause different versions of a trait to appear as the organism's phenotype.
- 23: A dominant allele causes its version of the trait to appear even when the organism also has a recessive allele for the gene.
- 24: In pea plants, the F allele, which causes purple flowers, is dominant over the f allele.
- 25: A pea plant with at least one F allele will have the F allele's version of the flower color trait.
- 26: So, a plant with the genotype FF or Ff will have purple flowers.
- 27: A recessive allele causes its version of the trait to appear only when the organism does not have any dominant alleles for the gene.
- 28: In pea plants, the f allele, which causes white flowers, is recessive to the F allele.
- 29: A pea plant with only f alleles will have the f allele's version of the flower color trait.
- 30: So, a plant with the genotype ff will have white flowers.
- 31: You need to determine the rose plant's phenotype for the thorns trait.
- 32: First, consider the alleles in the plant's genotype for the thorns gene.
- 33: Then, decide whether these alleles are dominant or recessive.
- 34: The allele for having thorns (R) is dominant over the allele for not having thorns (r).
- 35: This means R is a dominant allele, and r is a recessive allele.
- 36: The rose plant's genotype of Rr has one dominant allele and one recessive allele.
- 37: An organism with at least one dominant allele for a gene will have the dominant allele's version of the trait.
- 38: So, the rose plant's phenotype for the thorns trait must be not having thorns.
- 39: The answer is B.
id: 8928
question: Complete the sentence. Making lemonade is a ().
choice: (A) physical change (B) chemical change
gold answer: A
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: Chemical changes and physical changes are two ways matter can change.
- 1: In a chemical change, the type of matter changes.
- 2: Burning a piece of paper is a chemical change.
- 3: The paper changes into ash and smoke.
- 4: In a physical change, the type of matter stays the same.
- 5: Cutting a piece of paper is a physical change.
- 6: The cut pieces are still made of paper.
- 7: Ice melting is also a physical change.
- 8: When ice melts, it changes from a solid to a liquid.
- 9: But both ice and liquid water are made of the same type of matter: water!
- 10: This kind of change is called a change of state.
- 11: Making lemonade is a chemical change.
- 12: Lemonade is made by mixing lemon juice, sugar, and water.
- 13: The sugar and water make the lemon juice into a different type of matter.
- 14: The answer is B.
id: 9076
question: Will these magnets attract or repel each other?
choice: (A) repel (B) attract
context: Two magnets are placed as shown.

gold answer: A
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: Magnets can pull or push on each other without touching.
- 1: When magnets attract, they pull together.
- 2: When magnets repel, they push apart.
- 3: Whether a magnet attracts or repels other magnets depends on the positions of its poles, or ends.
- 4: Every magnet has two poles: north and south.
- 5: Here are some examples of magnets.
- 6: The north pole of each magnet is labeled N, and the south pole is labeled S. If opposite poles are closest to each other, the magnets attract.
- 7: The magnets in the pair below attract.
- 8: If the same, or like, poles are closest to each other, the magnets repel.
- 9: The magnets in both pairs below repel.
- 10: To predict if these magnets will attract or repel, look at which poles are closest to each other.
- 11: The north pole of one magnet is closest to the south pole of the other magnet.
- 12: Opposite poles attract.
- 13: So, these magnets will attract each other.
- 14: The answer is B.
id: 9110
question: Which animal's mouth is also adapted for bottom feeding?
choice: (A) orangespine unicornfish (B) sturgeon
context: Leopard sharks eat organisms such as crabs, shrimp, and fish. They are bottom feeders. Bottom feeders find their food at the bottom of rivers, lakes, and the ocean. The 's mouth is located on the underside of its head and points downward. Its mouth is adapted for bottom feeding. Figure: leopard shark.

gold answer: B
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: An adaptation is an inherited trait that helps an organism survive or reproduce.
- 1: Adaptations can include both body parts and behaviors.
- 2: The shape of an animal's mouth is one example of an adaptation.
- 3: Animals' mouths can be adapted in different ways.
- 4: For example, a large mouth with sharp teeth might help an animal tear through meat.
- 5: A long, thin mouth might help an animal catch insects that live in holes.
- 6: Animals that eat similar food often have similar mouths.
- 7: Look at the picture of the leopard shark.
- 8: The leopard shark's mouth is located on the underside of its head and points downward.
- 9: Its mouth is adapted for bottom feeding.
- 10: The leopard shark uses its mouth to find food hidden in the sediment of the ocean floor.
- 11: Now look at each animal.
- 12: Figure out which animal has a similar adaptation.
- 13: The orangespine unicornfish's mouth is located on the underside of its head and points downward.
- 14: Its mouth is adapted for bottom feeding.
- 15: The sturgeon's mouth is not located on the underside of its head.
- 16: Its mouth is not adapted for bottom feeding.
- 17: The answer is A.