id: 10102
question: Which word does not rhyme?
choice: (A) dine (B) heat (C) mine
gold answer: B
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: Rhyming words are words that end with the same sound.
- 1: The words tip and slip rhyme.
- 2: They both end with the same sound.
- 3: The words meet and treat also rhyme.
- 4: They both end with the same sound, even though the sound has two different spellings.
- 5: The words tip and meet don't rhyme.
- 6: They end with different sounds.
- 7: The words heat and mine rhyme.
- 8: They both end with the ate sound.
- 9: The word dine does not rhyme.
- 10: It ends with a different sound.
- 11: The answer is A.
id: 10157
question: Which of the following organisms is the tertiary consumer in this food web?
choice: (A) black racer (B) silver maple (C) beaver (D) black bear
context: Below is a food web from Shenandoah National Park, a forest ecosystem in Virginia. A food web models how the matter eaten by organisms moves through an ecosystem. The arrows in a food web represent how matter moves between organisms in an ecosystem.
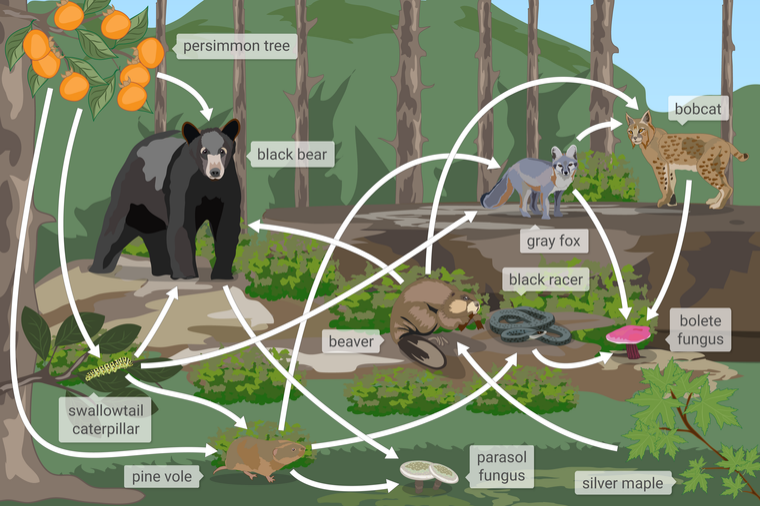
gold answer: A
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: A food web is a model.
- 1: A food web shows where organisms in an ecosystem get their food.
- 2: Models can make things in nature easier to understand because models can represent complex things in a simpler way.
- 3: If a food web showed every organism in an ecosystem, the food web would be hard to understand.
- 4: So, each food web shows how some organisms in an ecosystem can get their food.
- 5: Arrows show how matter moves.
- 6: A food web has arrows that point from one organism to another.
- 7: Each arrow shows the direction that matter moves when one organism eats another organism.
- 8: An arrow starts from the organism that is eaten.
- 9: The arrow points to the organism that is doing the eating.
- 10: An organism in a food web can have more than one arrow pointing from it.
- 11: This shows that the organism is eaten by more than one other organism in the food web.
- 12: An organism in a food web can also have more than one arrow pointing to it.
- 13: This shows that the organism eats more than one other organism in the food web.
- 14: Tertiary consumers eat secondary consumers.
- 15: So, in a food web, tertiary consumers have arrows pointing to them from secondary consumers.
- 16: Secondary consumers have arrows pointing to them from primary consumers.
- 17: And primary consumers have arrows pointing to them from producers.
- 18: The beaver has an arrow pointing to it from the silver maple.
- 19: The silver maple is not a secondary consumer, so the beaver is not a tertiary consumer.
- 20: The silver maple does not have any arrows pointing to it.
- 21: So, the silver maple is not a tertiary consumer.
- 22: The black racer has an arrow pointing to it from the pine vole.
- 23: The pine vole is not a secondary consumer, so the black racer is not a tertiary consumer.
- 24: The black bear has an arrow pointing to it from the pine vole.
- 25: The pine vole is a secondary consumer, so the black bear is a tertiary consumer.
- 26: The black bear has arrows pointing to it from the pine vole and the persimmon tree.
- 27: The persimmon tree is not a secondary consumer, so the black bear is a tertiary consumer.
- 28: The answer is D.
id: 10200
question: Which word would you find on a dictionary page with the following guide words? clutch - curse
choice: (A) capitol (B) criminal
gold answer: B
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: Guide words appear on each page of a dictionary.
- 1: They tell you the first word and last word on the page.
- 2: The other words on the page come between the guide words in alphabetical order.
- 3: To put words in alphabetical order, put them in order by their first letters.
- 4: If the first letters are the same, look at the second letters.
- 5: If the second letters are the same, look at the third letters, and so on.
- 6: If one word is shorter, and there are no more letters to compare, then the shorter word comes first in alphabetical order.
- 7: For example, be comes before bed.
- 8: Put the words in alphabetical order.
- 9: Since capitol is between the guide words clutch - curse, it would be found on that page.
- 10: The answer is A.
id: 10498
question: Which property do these four objects have in common?
choice: (A) sweet (B) fragile (C) opaque
context: Select the best answer.

gold answer: B
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: An object has different properties.
- 1: A property of an object can tell you how it looks, feels, tastes, or smells.
- 2: Properties can also tell you how an object will behave when something happens to it.
- 3: Different objects can have properties in common.
- 4: You can use these properties to put objects into groups.
- 5: Grouping objects by their properties is called classification.
- 6: Look at each object.
- 7: For each object, decide if it has that property.
- 8: An opaque object does not let light through.
- 9: The ceramic bottle is opaque, but the caramel corn and the apple juice are not.
- 10: Sugar has a sweet taste.
- 11: All four objects are sweet.
- 12: A fragile object will break into pieces if you drop it.
- 13: The ceramic bottle is fragile, but the caramel corn is not.
- 14: The property that all four objects have in common is sweet.
- 15: The answer is A.
id: 10520
question: Which three months have the same average precipitation?
choice: (A) June, July, and August (B) September, October, and November (C) March, April, and May
context: Use the graph to answer the question below.
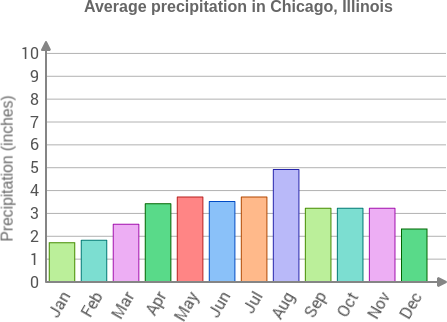
gold answer: B
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: Scientists record climate data from places around the world.
- 1: Precipitation, or rain and snow, is one type of climate data.
- 2: A bar graph can be used to show the average amount of precipitation each month.
- 3: Months with taller bars have more precipitation on average.
- 4: To describe the average precipitation trends in Chicago, look at the graph.
- 5: Choice "Mar" is incorrect.
- 6: Choice "Apr" is incorrect.
- 7: Choice "May" is incorrect.
- 8: Choice "Jun" is incorrect.
- 9: Choice "Jul" is incorrect.
- 10: Choice "Aug" is incorrect.
- 11: Choice "Sep" is incorrect.
- 12: Choice "Oct" is incorrect.
- 13: Choice "Nov" is incorrect.
- 14: June, July, and August each have an average precipitation of less than 3 inches.
- 15: Every other month has an average precipitation that is either greater than 3 inches or less than 2 inches.
- 16: So, June, July, and August have the same average precipitation.
- 17: The answer is A.
id: 10559
question: Think about the magnetic force between the magnets in each pair. Which of the following statements is true?
choice: (A) The magnitude of the magnetic force is the same in both pairs. (B) The magnitude of the magnetic force is greater in Pair 2. (C) The magnitude of the magnetic force is greater in Pair 1.
context: The images below show two pairs of magnets. The magnets in different pairs do not affect each other. All the magnets shown are made of the same material, but some of them are different shapes.
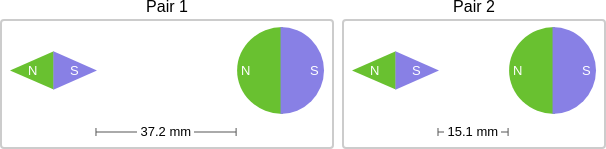
gold answer: B
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: Magnets can pull or push on each other without touching.
- 1: When magnets attract, they pull together.
- 2: When magnets repel, they push apart.
- 3: These pulls and pushes between magnets are called magnetic forces.
- 4: The strength of a force is called its magnitude.
- 5: The greater the magnitude of the magnetic force between two magnets, the more strongly the magnets attract or repel each other.
- 6: You can change the magnitude of a magnetic force between two magnets by changing the distance between them.
- 7: The magnitude of the magnetic force is greater when there is a smaller distance between the magnets.
- 8: Distance affects the magnitude of the magnetic force.
- 9: When there is a smaller distance between magnets, the magnitude of the magnetic force between them is greater.
- 10: There is a smaller distance between the magnets in Pair 1 than in Pair 2.
- 11: So, the magnitude of the magnetic force is greater in Pair 1 than in Pair 2.
- 12: The answer is C.
id: 10599
question: Will these magnets attract or repel each other?
choice: (A) repel (B) attract
context: Two magnets are placed as shown. Hint: Magnets that attract pull together. Magnets that repel push apart.

gold answer: A
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: Magnets can pull or push on each other without touching.
- 1: When magnets attract, they pull together.
- 2: When magnets repel, they push apart.
- 3: Whether a magnet attracts or repels other magnets depends on the positions of its poles, or ends.
- 4: Every magnet has two poles, called north and south.
- 5: Here are some examples of magnets.
- 6: The north pole of each magnet is marked N, and the south pole is marked S. If different poles are closest to each other, the magnets attract.
- 7: The magnets in the pair below attract.
- 8: If the same poles are closest to each other, the magnets repel.
- 9: The magnets in both pairs below repel.
- 10: Will these magnets attract or repel?
- 11: To find out, look at which poles are closest to each other.
- 12: The north pole of one magnet is closest to the south pole of the other magnet.
- 13: Poles that are different attract.
- 14: So, these magnets will attract each other.
- 15: The answer is B.
id: 10659
question: Which of these organisms contains matter that was once part of the bear sedge?
choice: (A) grizzly bear (B) earthworm (C) mushroom
context: Below is a food web from a tundra ecosystem in Nunavut, a territory in Northern Canada. A food web models how the matter eaten by organisms moves through an ecosystem. The arrows in a food web represent how matter moves between organisms in an ecosystem.
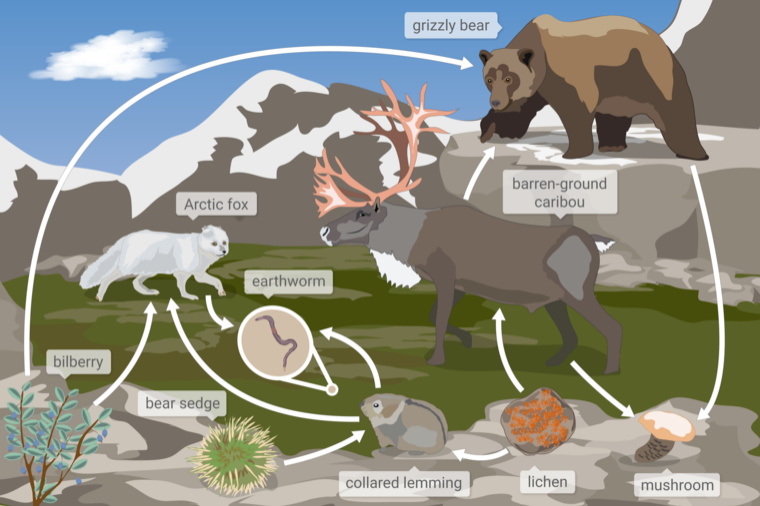
gold answer: B
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: A food web is a model.
- 1: A food web shows where organisms in an ecosystem get their food.
- 2: Models can make things in nature easier to understand because models can represent complex things in a simpler way.
- 3: If a food web showed every organism in an ecosystem, the food web would be hard to understand.
- 4: So, each food web shows how some organisms in an ecosystem can get their food.
- 5: Arrows show how matter moves.
- 6: A food web has arrows that point from one organism to another.
- 7: Each arrow shows the direction that matter moves when one organism eats another organism.
- 8: An arrow starts from the organism that is eaten.
- 9: The arrow points to the organism that is doing the eating.
- 10: An organism in a food web can have more than one arrow pointing from it.
- 11: This shows that the organism is eaten by more than one other organism in the food web.
- 12: An organism in a food web can also have more than one arrow pointing to it.
- 13: This shows that the organism eats more than one other organism in the food web.
- 14: Use the arrows to follow how matter moves through this food web.
- 15: For each answer choice, try to find a path of arrows that starts from the bear sedge.
- 16: The only arrow pointing to the grizzly bear starts from the bilberry.
- 17: The bilberry does not have an arrow pointing to it.
- 18: So, in this food web, matter does not move from the bear sedge to the grizzly bear.
- 19: The only arrow pointing to the mushroom starts from the earthworm.
- 20: The earthworm does not have an arrow pointing to it.
- 21: So, in this food web, matter does not move from the bear sedge to the mushroom.There are two paths matter can take from the bear sedge to the collared lemming: bear sedge->collared lemming.
- 22: bear sedge->brown lemming->collared lemming.
- 23: There is one path matter can take from the bear sedge to the parasitic jaeger: bear sedge->parasitic jaeger.
- 24: The answer is C.
id: 10715
question: Which of the following best describes a community in a New Zealand kelp forest?
choice: (A) the rocks and the bull kelp (B) a group of New Zealand sea lions (C) the sea stars, the crabs, and the snails
context: Read the passage. Then answer the question below. Bull kelp, a species of large seaweed, forms thick kelp forests along the coast of New Zealand. Kelp forests are home to many species, including the New Zealand sea lion. These sea lions hunt octopus and squid that live in the kelp forest. The individual kelp stalks have strong holdfasts, or root-like structures, that cling tightly to the rocks on the seafloor. Small invertebrates such as sea stars, crabs, and snails can live on or around the holdfasts. Figure: a kelp holdfast attached to a rock.

gold answer: C
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: In an environment, organisms interact with each other and with their nonliving surroundings.
- 1: To help describe these interactions, ecologists use specific terms for different types of groups.
- 2: A single organism is an individual.
- 3: Individuals of the same species that live in the same place are part of a population.
- 4: Multiple populations of different species that live in the same place are part of a community.
- 5: Together, communities of living organisms and the nonliving parts of their environment make up an ecosystem.
- 6: The answer is A.
id: 10722
question: Which solution has a higher concentration of green particles?
choice: (A) Solution A (B) Solution B (C) neither; their concentrations are the same
context: The diagram below is a model of two solutions. Each green ball represents one particle of solute.
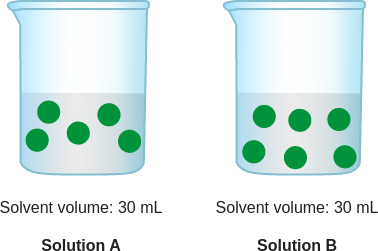
gold answer: B
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: A solution is made up of two or more substances that are completely mixed.
- 1: In a solution, solute particles are mixed into a solvent.
- 2: The solute cannot be separated from the solvent by a filter.
- 3: For example, if you stir a spoonful of salt into a cup of water, the salt will mix into the water to make a saltwater solution.
- 4: In this case, the salt is the solute.
- 5: The water is the solvent.
- 6: The concentration of a solute in a solution is a measure of the ratio of solute to solvent.
- 7: Concentration can be described in terms of particles of solute per volume of solvent.
- 8: concentration = particles of solute / volume of solvent In Solution A and Solution B, the green particles represent the solute.
- 9: To figure out which solution has a higher concentration of green particles, look at both the number of green particles and the volume of the solvent in each container.
- 10: Use the concentration formula to find the number of green particles per milliliter.
- 11: Solution A has more green particles per milliliter.
- 12: So, Solution A has a higher concentration of green particles.
- 13: The answer is A.