id: 4563
question: Which figure of speech is used in this text? In every cry of every Man, In every Infant's cry of fear, In every voice: in every ban, The mind-forg'd manacles I hear. —William Blake, "London"
choice: (A) anaphora (B) assonance
gold answer: A
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: Figures of speech are words or phrases that use language in a nonliteral or unusual way.
- 1: They can make writing more expressive.
- 2: Anaphora is the repetition of the same word or words at the beginning of several phrases or clauses.
- 3: We are united.
- 4: We are powerful.
- 5: We are winners.
- 6: Antithesis involves contrasting opposing ideas within a parallel grammatical structure.
- 7: I want to help, not to hurt.
- 8: Apostrophe is a direct address to an absent person or a nonhuman entity.
- 9: Oh, little bird, what makes you sing so beautifully?
- 10: Assonance is the repetition of a vowel sound in a series of nearby words.
- 11: Try to light the fire.
- 12: Chiasmus is an expression in which the second half parallels the first but reverses the order of words.
- 13: Never let a fool kiss you or a kiss fool you.
- 14: Understatement involves deliberately representing something as less serious or important than it really is.
- 15: As you know, it can get a little cold in the Antarctic.
- 16: The text uses assonance, the repetition of a vowel sound in a series of nearby words.
- 17: The words cry, Infant's, every, and voice share a vowel sound.
- 18: The answer is B.
id: 4580
question: Which i in column 3?
choice: (A) the library (B) the park (C) the restaurant (D) the police department
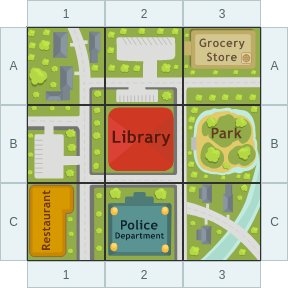
gold answer: B
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: A grid is made up of lines of squares.
- 1: They are organized in rows and columns.
- 2: A grid can help you use a map.
- 3: A row is a line of squares that goes from side to side.
- 4: Rows are marked with letters.
- 5: A column is a line of squares that goes up and down.
- 6: Columns are marked with numbers.
- 7: The police department is in column 3.
- 8: The answer is D.
id: 4621
question: Which word would you find on a dictionary page with the following guide words? wave - which
choice: (A) wear (B) women
gold answer: A
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: Guide words appear on each page of a dictionary.
- 1: They tell you the first word and last word on the page.
- 2: The other words on the page come between the guide words in alphabetical order.
- 3: To put words in alphabetical order, put them in order by their first letters.
- 4: If the first letters are the same, look at the second letters.
- 5: If the second letters are the same, look at the third letters, and so on.
- 6: If one word is shorter, and there are no more letters to compare, then the shorter word comes first in alphabetical order.
- 7: For example, be comes before bed.
- 8: Put the words in alphabetical order.
- 9: Since women is between the guide words wave - which, it would be found on that page.
- 10: The answer is B.
id: 4776
question: Would you find the word pliers on a dictionary page with the following guide words? peaceful - power
choice: (A) no (B) yes
gold answer: B
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: Guide words appear on each page of a dictionary.
- 1: They tell you the first word and last word on the page.
- 2: The other words on the page come between the guide words in alphabetical order.
- 3: To put words in alphabetical order, put them in order by their first letters.
- 4: If the first letters are the same, look at the second letters.
- 5: If the second letters are the same, look at the third letters, and so on.
- 6: If one word is shorter, and there are no more letters to compare, then the shorter word comes first in alphabetical order.
- 7: For example, be comes before bed.
- 8: Put the words in alphabetical order.
- 9: Since pliers is not between the guide words peaceful - power, it would not be found on that page.
- 10: The answer is A.
id: 4794
question: Will these magnets attract or repel each other?
choice: (A) repel (B) attract
context: Two magnets are placed as shown.

gold answer: A
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: Magnets can pull or push on each other without touching.
- 1: When magnets attract, they pull together.
- 2: When magnets repel, they push apart.
- 3: Whether a magnet attracts or repels other magnets depends on the positions of its poles, or ends.
- 4: Every magnet has two poles: north and south.
- 5: Here are some examples of magnets.
- 6: The north pole of each magnet is labeled N, and the south pole is labeled S. If opposite poles are closest to each other, the magnets attract.
- 7: The magnets in the pair below attract.
- 8: If the same, or like, poles are closest to each other, the magnets repel.
- 9: The magnets in both pairs below repel.
- 10: To predict if these magnets will attract or repel, look at which poles are closest to each other.
- 11: The north pole of one magnet is closest to the south pole of the other magnet.
- 12: Opposite poles attract.
- 13: So, these magnets will attract each other.
- 14: The answer is B.
id: 4799
question: Which property do these three objects have in common?
choice: (A) flexible (B) colorful (C) salty
context: Select the best answer.

gold answer: B
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: An object has different properties.
- 1: A property of an object can tell you how it looks, feels, tastes, or smells.
- 2: Properties can also tell you how an object will behave when something happens to it.
- 3: Different objects can have properties in common.
- 4: You can use these properties to put objects into groups.
- 5: Grouping objects by their properties is called classification.
- 6: Look at each object.
- 7: For each object, decide if it has that property.
- 8: A flexible object can be folded or bent without breaking easily.
- 9: All three objects are flexible.
- 10: A colorful object has one or more bright colors.
- 11: The pretzel and the cracker are not colorful.
- 12: Potato chips have a salty taste.
- 13: The rainbow sucker is not salty.
- 14: The property that all three objects have in common is flexible.
- 15: The answer is A.
id: 4913
question: Will these magnets attract or repel each other?
choice: (A) attract (B) repel
context: Two magnets are placed as shown.

gold answer: B
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: Magnets can pull or push on other magnets without touching them.
- 1: When magnets attract, they pull together.
- 2: When magnets repel, they push apart.
- 3: These pulls and pushes are called magnetic forces.
- 4: Magnetic forces are strongest at the magnets' poles, or ends.
- 5: Every magnet has two poles: a north pole (N) and a south pole (S).
- 6: Here are some examples of magnets.
- 7: Their poles are shown in different colors and labeled.
- 8: Whether a magnet attracts or repels other magnets depends on the positions of its poles.
- 9: If opposite poles are closest to each other, the magnets attract.
- 10: The magnets in the pair below attract.
- 11: If the same, or like, poles are closest to each other, the magnets repel.
- 12: The magnets in both pairs below repel.
- 13: To predict if these magnets will attract or repel, look at which poles are closest to each other.
- 14: The north pole of one magnet is closest to the south pole of the other magnet.
- 15: Opposite poles attract.
- 16: So, these magnets will attract each other.
- 17: The answer is A.
id: 5053
question: Which word would you find on a dictionary page with the following guide words? careful - cocoa
choice: (A) curve (B) chord
gold answer: B
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: Guide words appear on each page of a dictionary.
- 1: They tell you the first word and last word on the page.
- 2: The other words on the page come between the guide words in alphabetical order.
- 3: To put words in alphabetical order, put them in order by their first letters.
- 4: If the first letters are the same, look at the second letters.
- 5: If the second letters are the same, look at the third letters, and so on.
- 6: If one word is shorter, and there are no more letters to compare, then the shorter word comes first in alphabetical order.
- 7: For example, be comes before bed.
- 8: Put the words in alphabetical order.
- 9: Since curve is between the guide words careful - cocoa, it would be found on that page.
- 10: The answer is A.
id: 5085
question: Which trait did Tripneustes have? Select the trait you can observe on the fossil.
choice: (A) white spines covering its body (B) a reddish-orange body (C) a rounded body
context: This picture shows a fossil of an ancient animal called Tripneustes. Fossils of Tripneustes have been found in rocks that are more than 20,000,000 years old.

gold answer: C
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: The way an organism looks or acts is called a trait.
- 1: Scientists use fossils to learn more about the traits of ancient organisms.
- 2: Fossils can preserve the remains of body parts and activities.
- 3: A fossil of a body part, such as a tail or a wing, can tell you what an organism looked like.
- 4: A fossil of an organism's activities, such as a burrow or a footprint, can tell you about the organism's behavior.
- 5: Here are three examples of fossils and the traits that you can observe from them: This is a fossil of an animal.
- 6: This fossil tells you that the animal had a spiral-shaped shell.
- 7: This is a fossil of a plant.
- 8: This fossil tells you that the plant had small leaves arranged in a branched pattern.
- 9: This is a fossil of an animal's footprint.
- 10: This fossil tells you that the animal could walk on land.
- 11: An organism's fossil may not show all of the organism's traits.
- 12: This is because most body parts are destroyed during fossil formation.
- 13: When an organism's body turns into a fossil, only a few body parts are usually preserved.
- 14: The answer is A.
id: 5114
question: Which of these organisms contains matter that was once part of the bilberry?
choice: (A) barren-ground caribou (B) rough-legged hawk (C) bear sedge (D) lichen
context: Below is a food web from a tundra ecosystem in Nunavut, a territory in Northern Canada. A food web models how the matter eaten by organisms moves through an ecosystem. The arrows in a food web represent how matter moves between organisms in an ecosystem.
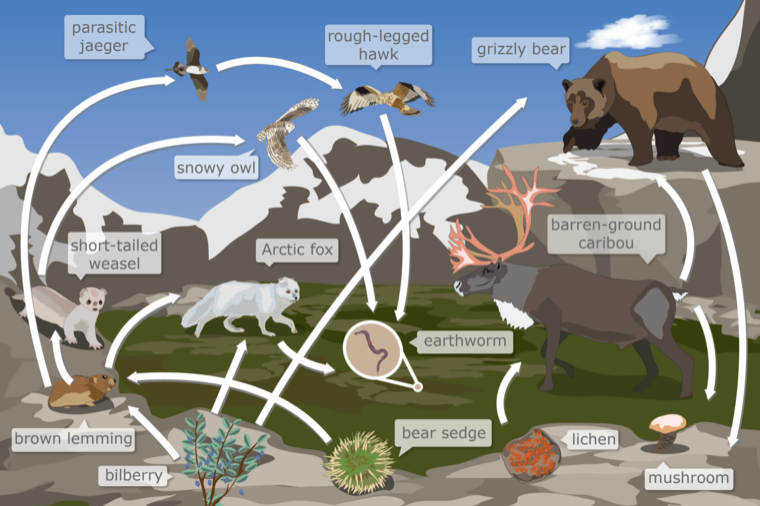
gold answer: B
wrong prediction:
Rationale:
- 0: A food web is a model.
- 1: A food web shows where organisms in an ecosystem get their food.
- 2: Models can make things in nature easier to understand because models can represent complex things in a simpler way.
- 3: If a food web showed every organism in an ecosystem, the food web would be hard to understand.
- 4: So, each food web shows how some organisms in an ecosystem can get their food.
- 5: Arrows show how matter moves.
- 6: A food web has arrows that point from one organism to another.
- 7: Each arrow shows the direction that matter moves when one organism eats another organism.
- 8: An arrow starts from the organism that is eaten.
- 9: The arrow points to the organism that is doing the eating.
- 10: An organism in a food web can have more than one arrow pointing from it.
- 11: This shows that the organism is eaten by more than one other organism in the food web.
- 12: An organism in a food web can also have more than one arrow pointing to it.
- 13: This shows that the organism eats more than one other organism in the food web.
- 14: Use the arrows to follow how matter moves through this food web.
- 15: For each answer choice, try to find a path of arrows that starts from the bilberry.There is one path matter can take from the bilberry to the bear sedge: bilberry->bear sedge.
- 16: lichen.
- 17: The lichen does not have any arrows pointing to it.
- 18: So, in this food web, matter does not move from the bilberry to the lichen.. barren-ground caribou.
- 19: The only arrow pointing to the barren-ground caribou starts from the lichen.
- 20: The lichen does not have any arrows pointing to it.
- 21: So, in this food web, matter does not move from the bilberry to the barren-ground caribou..
- 22: There are two paths matter can take from the bilberry to the grizzly bear: bilberry->bear sedge->grizzly bear.
- 23: bilberry->brown lemming->grizzly bear.
- 24: rough-legged hawk.
- 25: The rough-legged hawk has two arrows pointing to it.
- 26: One arrow starts from the parasitic jaeger.
- 27: The other arrow starts from the brown lemming.
- 28: The brown lemming has two arrows pointing to it.
- 29: One arrow starts from the bilberry.
- 30: The other arrow starts from the bear sedge.
- 31: The bear sedge does not have any arrows pointing to it.
- 32: So, in this food web, matter does not move from the bilberry to the rough-legged hawk..
- 33: The answer is C.