id: 4794
lecture: Magnets can pull or push on other magnets without touching them. When magnets attract, they pull together. When magnets repel, they push apart. These pulls and pushes are called magnetic forces. Magnetic forces are strongest at the magnets' poles, or ends. Every magnet has two poles: a north pole (N) and a south pole (S). Here are some examples of magnets. Their poles are shown in different colors and labeled. Whether a magnet attracts or repels other magnets depends on the positions of its poles. If opposite poles are closest to each other, the magnets attract. The magnets in the pair below attract. If the same, or like, poles are closest to each other, the magnets repel. The magnets in both pairs below repel.
question: Will these magnets attract or repel each other?
choice: (A) repel (B) attract
context: Two magnets are placed as shown.

answer: A
Rationale:
- 0: Magnets can pull or push on each other without touching.
- 1: When magnets attract, they pull together.
- 2: When magnets repel, they push apart.
- 3: Whether a magnet attracts or repels other magnets depends on the positions of its poles, or ends.
- 4: Every magnet has two poles: north and south.
- 5: Here are some examples of magnets.
- 6: The north pole of each magnet is labeled N, and the south pole is labeled S. If opposite poles are closest to each other, the magnets attract.
- 7: The magnets in the pair below attract.
- 8: If the same, or like, poles are closest to each other, the magnets repel.
- 9: The magnets in both pairs below repel.
- 10: To predict if these magnets will attract or repel, look at which poles are closest to each other.
- 11: The north pole of one magnet is closest to the south pole of the other magnet.
- 12: Opposite poles attract.
- 13: So, these magnets will attract each other.
- 14: The answer is B.
generated_skill: The missing skill in this scenario is the ability to identify and analyze the positions of the poles on magnets to determine whether they will attract or repel each other.
solution: To predict if these magnets will attract or repel, look at which poles are closest to each other. The north pole of one magnet is closest to the north pole of the other magnet. Like poles repel. So, these magnets will repel each other.
skill: Identify magnets that attract or repel
wrong_step_idx: 11
id: 4799
lecture: An object has different properties. A property of an object can tell you how it looks, feels, tastes, or smells. Properties can also tell you how an object will behave when something happens to it. Different objects can have properties in common. You can use these properties to put objects into groups. Grouping objects by their properties is called classification.
question: Which property do these three objects have in common?
choice: (A) flexible (B) colorful (C) salty
context: Select the best answer.

answer: B
Rationale:
- 0: An object has different properties.
- 1: A property of an object can tell you how it looks, feels, tastes, or smells.
- 2: Properties can also tell you how an object will behave when something happens to it.
- 3: Different objects can have properties in common.
- 4: You can use these properties to put objects into groups.
- 5: Grouping objects by their properties is called classification.
- 6: Look at each object.
- 7: For each object, decide if it has that property.
- 8: A flexible object can be folded or bent without breaking easily.
- 9: All three objects are flexible.
- 10: A colorful object has one or more bright colors.
- 11: The pretzel and the cracker are not colorful.
- 12: Potato chips have a salty taste.
- 13: The rainbow sucker is not salty.
- 14: The property that all three objects have in common is flexible.
- 15: The answer is A.
generated_skill: The missing skill in this case is the ability to identify the correct property that is common among the three objects. The wrong rationale incorrectly identifies flexibility as the common property, when in fact the common property is being colorful. The assistant needs to be able to accurately analyze the properties of the objects and correctly identify the common property.
solution: Look at each object. For each object, decide if it has that property. Potato chips have a salty taste. The rainbow sucker is not salty. A colorful object has one or more bright colors. All three objects are colorful. A flexible object can be folded or bent without breaking easily. The flip-flops and the silk tie are flexible, but the rainbow sucker is not. The property that all three objects have in common is colorful.
skill: Compare properties of objects
wrong_step_idx: 9
id: 4913
lecture: Magnets can pull or push on each other without touching. When magnets attract, they pull together. When magnets repel, they push apart. Whether a magnet attracts or repels other magnets depends on the positions of its poles, or ends. Every magnet has two poles: north and south. Here are some examples of magnets. The north pole of each magnet is labeled N, and the south pole is labeled S. If opposite poles are closest to each other, the magnets attract. The magnets in the pair below attract. If the same, or like, poles are closest to each other, the magnets repel. The magnets in both pairs below repel.
question: Will these magnets attract or repel each other?
choice: (A) attract (B) repel
context: Two magnets are placed as shown.

answer: B
Rationale:
- 0: Magnets can pull or push on other magnets without touching them.
- 1: When magnets attract, they pull together.
- 2: When magnets repel, they push apart.
- 3: These pulls and pushes are called magnetic forces.
- 4: Magnetic forces are strongest at the magnets' poles, or ends.
- 5: Every magnet has two poles: a north pole (N) and a south pole (S).
- 6: Here are some examples of magnets.
- 7: Their poles are shown in different colors and labeled.
- 8: Whether a magnet attracts or repels other magnets depends on the positions of its poles.
- 9: If opposite poles are closest to each other, the magnets attract.
- 10: The magnets in the pair below attract.
- 11: If the same, or like, poles are closest to each other, the magnets repel.
- 12: The magnets in both pairs below repel.
- 13: To predict if these magnets will attract or repel, look at which poles are closest to each other.
- 14: The north pole of one magnet is closest to the south pole of the other magnet.
- 15: Opposite poles attract.
- 16: So, these magnets will attract each other.
- 17: The answer is A.
generated_skill: The missing skill is the ability to determine the positions of the poles on the magnets and how they interact with each other.
solution: To predict if these magnets will attract or repel, look at which poles are closest to each other. The north pole of one magnet is closest to the north pole of the other magnet. Like poles repel. So, these magnets will repel each other.
skill: Identify magnets that attract or repel
wrong_step_idx: 14
id: 5053
lecture: Guide words appear on each page of a dictionary. They tell you the first word and last word on the page. The other words on the page come between the guide words in alphabetical order. To put words in alphabetical order, put them in order by their first letters. If the first letters are the same, look at the second letters. If the second letters are the same, look at the third letters, and so on. If one word is shorter, and there are no more letters to compare, then the shorter word comes first in alphabetical order. For example, be comes before bed.
question: Which word would you find on a dictionary page with the following guide words? careful - cocoa
choice: (A) curve (B) chord
context: N/A
answer: B
Rationale:
- 0: Guide words appear on each page of a dictionary.
- 1: They tell you the first word and last word on the page.
- 2: The other words on the page come between the guide words in alphabetical order.
- 3: To put words in alphabetical order, put them in order by their first letters.
- 4: If the first letters are the same, look at the second letters.
- 5: If the second letters are the same, look at the third letters, and so on.
- 6: If one word is shorter, and there are no more letters to compare, then the shorter word comes first in alphabetical order.
- 7: For example, be comes before bed.
- 8: Put the words in alphabetical order.
- 9: Since curve is between the guide words careful - cocoa, it would be found on that page.
- 10: The answer is A.
generated_skill: The missing skill in this query is understanding how to use guide words in a dictionary to determine the placement of a word. The user incorrectly assumes that the shorter word comes first in alphabetical order, leading to the wrong answer.
solution: Put the words in alphabetical order. Since chord is between the guide words careful - cocoa, it would be found on that page.
skill: Use guide words
wrong_step_idx: 9
id: 5085
lecture: The way an organism looks or acts is called a trait. Scientists use fossils to learn more about the traits of ancient organisms. Fossils can preserve the remains of body parts and activities. A fossil of a body part, such as a tail or a wing, can tell you what an organism looked like. A fossil of an organism's activities, such as a burrow or a footprint, can tell you about the organism's behavior. Here are three examples of fossils and the traits that you can observe from them: This is a fossil of an animal. This fossil tells you that the animal had a spiral-shaped shell. This is a fossil of a plant. This fossil tells you that the plant had small leaves arranged in a branched pattern. This is a fossil of an animal's footprint. This fossil tells you that the animal could walk on land. An organism's fossil may not show all of the organism's traits. This is because most body parts are destroyed during fossil formation. When an organism's body turns into a fossil, only a few body parts are usually preserved.
question: Which trait did Tripneustes have? Select the trait you can observe on the fossil.
choice: (A) white spines covering its body (B) a reddish-orange body (C) a rounded body
context: This picture shows a fossil of an ancient animal called Tripneustes. Fossils of Tripneustes have been found in rocks that are more than 20,000,000 years old.

answer: C
Rationale:
- 0: The way an organism looks or acts is called a trait.
- 1: Scientists use fossils to learn more about the traits of ancient organisms.
- 2: Fossils can preserve the remains of body parts and activities.
- 3: A fossil of a body part, such as a tail or a wing, can tell you what an organism looked like.
- 4: A fossil of an organism's activities, such as a burrow or a footprint, can tell you about the organism's behavior.
- 5: Here are three examples of fossils and the traits that you can observe from them: This is a fossil of an animal.
- 6: This fossil tells you that the animal had a spiral-shaped shell.
- 7: This is a fossil of a plant.
- 8: This fossil tells you that the plant had small leaves arranged in a branched pattern.
- 9: This is a fossil of an animal's footprint.
- 10: This fossil tells you that the animal could walk on land.
- 11: An organism's fossil may not show all of the organism's traits.
- 12: This is because most body parts are destroyed during fossil formation.
- 13: When an organism's body turns into a fossil, only a few body parts are usually preserved.
- 14: The answer is A.
generated_skill: The missing skill is the ability to identify the trait that can be observed on the fossil. The wrong rationale states that the answer is A because the fossil may not show all of the organism's traits and only a few body parts are usually preserved. However, the correct answer is C, which means that the missing skill is the ability to recognize and interpret the specific trait that is observable on the fossil, in this case, a rounded body.
solution:
skill: Compare fossils to modern organisms
wrong_step_idx: 14
id: 5114
lecture: A food web is a model. A food web shows where organisms in an ecosystem get their food. Models can make things in nature easier to understand because models can represent complex things in a simpler way. If a food web showed every organism in an ecosystem, the food web would be hard to understand. So, each food web shows how some organisms in an ecosystem can get their food. Arrows show how matter moves. A food web has arrows that point from one organism to another. Each arrow shows the direction that matter moves when one organism eats another organism. An arrow starts from the organism that is eaten. The arrow points to the organism that is doing the eating. An organism in a food web can have more than one arrow pointing from it. This shows that the organism is eaten by more than one other organism in the food web. An organism in a food web can also have more than one arrow pointing to it. This shows that the organism eats more than one other organism in the food web.
question: Which of these organisms contains matter that was once part of the bilberry?
choice: (A) barren-ground caribou (B) rough-legged hawk (C) bear sedge (D) lichen
context: Below is a food web from a tundra ecosystem in Nunavut, a territory in Northern Canada. A food web models how the matter eaten by organisms moves through an ecosystem. The arrows in a food web represent how matter moves between organisms in an ecosystem.
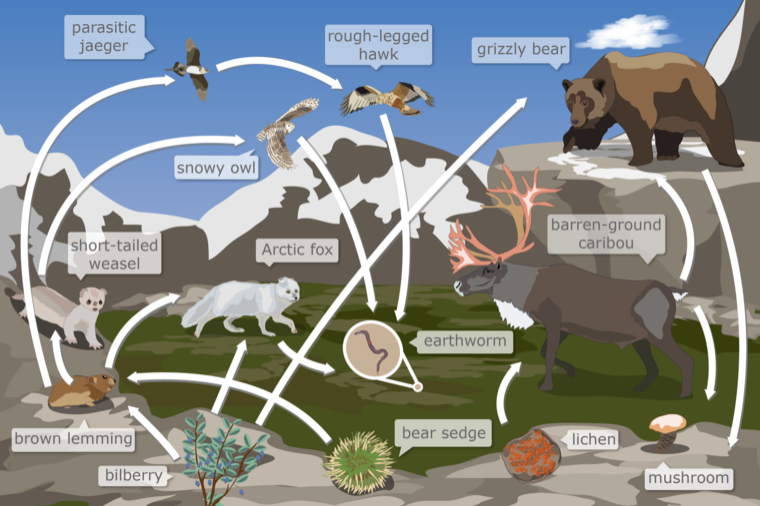
answer: B
Rationale:
- 0: A food web is a model.
- 1: A food web shows where organisms in an ecosystem get their food.
- 2: Models can make things in nature easier to understand because models can represent complex things in a simpler way.
- 3: If a food web showed every organism in an ecosystem, the food web would be hard to understand.
- 4: So, each food web shows how some organisms in an ecosystem can get their food.
- 5: Arrows show how matter moves.
- 6: A food web has arrows that point from one organism to another.
- 7: Each arrow shows the direction that matter moves when one organism eats another organism.
- 8: An arrow starts from the organism that is eaten.
- 9: The arrow points to the organism that is doing the eating.
- 10: An organism in a food web can have more than one arrow pointing from it.
- 11: This shows that the organism is eaten by more than one other organism in the food web.
- 12: An organism in a food web can also have more than one arrow pointing to it.
- 13: This shows that the organism eats more than one other organism in the food web.
- 14: Use the arrows to follow how matter moves through this food web.
- 15: For each answer choice, try to find a path of arrows that starts from the bilberry.There is one path matter can take from the bilberry to the bear sedge: bilberry->bear sedge.
- 16: lichen.
- 17: The lichen does not have any arrows pointing to it.
- 18: So, in this food web, matter does not move from the bilberry to the lichen.. barren-ground caribou.
- 19: The only arrow pointing to the barren-ground caribou starts from the lichen.
- 20: The lichen does not have any arrows pointing to it.
- 21: So, in this food web, matter does not move from the bilberry to the barren-ground caribou..
- 22: There are two paths matter can take from the bilberry to the grizzly bear: bilberry->bear sedge->grizzly bear.
- 23: bilberry->brown lemming->grizzly bear.
- 24: rough-legged hawk.
- 25: The rough-legged hawk has two arrows pointing to it.
- 26: One arrow starts from the parasitic jaeger.
- 27: The other arrow starts from the brown lemming.
- 28: The brown lemming has two arrows pointing to it.
- 29: One arrow starts from the bilberry.
- 30: The other arrow starts from the bear sedge.
- 31: The bear sedge does not have any arrows pointing to it.
- 32: So, in this food web, matter does not move from the bilberry to the rough-legged hawk..
- 33: The answer is C.
generated_skill: The missing skill in this case is the ability to identify the correct path of arrows in the food web that shows the transfer of matter from the bilberry to other organisms.
solution: Use the arrows to follow how matter moves through this food web. For each answer choice, try to find a path of arrows that starts from the bilberry. The bear sedge does not have any arrows pointing to it. So, in this food web, matter does not move from the bilberry to the bear sedge. The only arrow pointing to the barren-ground caribou starts from the lichen. The lichen does not have any arrows pointing to it. So, in this food web, matter does not move from the bilberry to the barren-ground caribou. The lichen does not have any arrows pointing to it. So, in this food web, matter does not move from the bilberry to the lichen.There are four paths matter can take from the bilberry to the earthworm: bilberry->Arctic fox->earthworm. bilberry->brown lemming->Arctic fox->earthworm. bilberry->brown lemming->snowy owl->earthworm. bilberry->brown lemming->parasitic jaeger->rough-legged hawk->earthworm. There is one path matter can take from the bilberry to the rough-legged hawk: bilberry->brown lemming->parasitic jaeger->rough-legged hawk.
skill: Interpret food webs II
wrong_step_idx: 15
id: 5191
lecture: Guide words appear on each page of a dictionary. They tell you the first word and last word on the page. The other words on the page come between the guide words in alphabetical order. To put words in alphabetical order, put them in order by their first letters. If the first letters are the same, look at the second letters. If the second letters are the same, look at the third letters, and so on. If one word is shorter, and there are no more letters to compare, then the shorter word comes first in alphabetical order. For example, be comes before bed.
question: Which word would you find on a dictionary page with the following guide words? path - polar
choice: (A) plum (B) push
context: N/A
answer: A
Rationale:
- 0: Guide words appear on each page of a dictionary.
- 1: They tell you the first word and last word on the page.
- 2: The other words on the page come between the guide words in alphabetical order.
- 3: To put words in alphabetical order, put them in order by their first letters.
- 4: If the first letters are the same, look at the second letters.
- 5: If the second letters are the same, look at the third letters, and so on.
- 6: If one word is shorter, and there are no more letters to compare, then the shorter word comes first in alphabetical order.
- 7: For example, be comes before bed.
- 8: Put the words in alphabetical order.
- 9: Since push is between the guide words path - polar, it would be found on that page.
- 10: The answer is B.
generated_skill: The model did not accurately understand how to determine the word that would be found on a dictionary page with the given guide words.
solution: Put the words in alphabetical order. Since plum is between the guide words path - polar, it would be found on that page.
skill: Use guide words
wrong_step_idx: 9
id: 5219
lecture: When writing, make sure to avoid vague pronoun references. A vague pronoun reference occurs when a pronoun could refer to more than one possible antecedent. When Lisa and Kim finally landed, she breathed a sigh of relief. The pronoun she could refer to either Lisa or Kim, so the meaning of the sentence is unclear. Vague pronoun references can be corrected in one of two ways: 1. Replace the pronoun with its correct antecedent: When Lisa and Kim finally landed, Lisa breathed a sigh of relief. 2. Rewrite the sentence: Lisa breathed a sigh of relief when she and Kim finally landed. A vague pronoun reference also occurs when they, them, their, theirs, it, or its is used without its antecedent. They say that this nail polish dries in less than five minutes. The pronoun they is used without its antecedent, so the meaning of the sentence is unclear. This problem can be fixed by replacing the pronoun with its missing antecedent. The advertisements say that this nail polish dries in less than five minutes.
question: Which of the following contains a vague pronoun reference?
choice: (A) If Danny winds up attending Adam's performance, he will let Susan know. (B) Danny will let Susan know if he winds up attending Adam's performance.
context: N/A
answer: A
Rationale:
- 0: When writing, make sure to avoid vague pronoun references.
- 1: A vague pronoun reference occurs when a pronoun could refer to more than one possible antecedent.
- 2: When Lisa and Kim finally landed, she breathed a sigh of relief.
- 3: The pronoun she could refer to either Lisa or Kim, so the meaning of the sentence is unclear.
- 4: Vague pronoun references can be corrected in one of two ways: 1.
- 5: Replace the pronoun with its correct antecedent: When Lisa and Kim finally landed, Lisa breathed a sigh of relief.
- 6: 2.
- 7: Rewrite the sentence: Lisa breathed a sigh of relief when she and Kim finally landed.
- 8: A vague pronoun reference also occurs when they, them, their, theirs, it, or its is used without its antecedent.
- 9: They say that this nail polish dries in less than five minutes.
- 10: The pronoun they is used without its antecedent, so the meaning of the sentence is unclear.
- 11: This problem can be fixed by replacing the pronoun with its missing antecedent.
- 12: The advertisements say that this nail polish dries in less than five minutes.
- 13: The second answer choice contains a vague pronoun reference.
- 14: The pronoun he could refer to Danny or Adam.
- 15: Danny will let Susan know if he winds up attending Adam's performance.
- 16: The first answer choice shows a possible correction for the vague pronoun reference.
- 17: The text has been rewritten so that the meaning is clear.
- 18: If Danny winds up attending Adam's performance, he will let Susan know.
- 19: The answer is B.
generated_skill: The missing skill is identifying and avoiding vague pronoun references in writing.
solution: The second answer choice contains a vague pronoun reference. The pronoun he could refer to Danny or Adam. If Danny winds up attending Adam's performance, he will let Susan know. The first answer choice shows a possible correction for the vague pronoun reference. The text has been rewritten so that the meaning is clear. Danny will let Susan know if he winds up attending Adam's performance.
skill: Identify vague pronoun references
wrong_step_idx: 13
id: 5345
lecture: A clause is a group of words that contains both a subject and a predicate. An independent clause is a complete thought that can stand alone as a sentence. A dependent clause (or subordinate clause) is not a complete thought and cannot stand alone as a sentence. the oranges on our tree are ripe The clause can stand alone. It is independent. after we pick up Kevin from work The clause cannot stand alone. It is dependent. A simple sentence is made up of a single independent clause. Ben and I spent all day relaxing by the pool. Some simple sentences have introductory phrases, but the introductory phrase is part of the predicate. In the winter, Ben usually wears his heavy coat. Ben usually wears his heavy coat in the winter. A compound sentence is made up of two independent clauses joined by a coordinating conjunction such as and, but, or, or so. We saw the flash of lightning, and seconds later we heard a rumble of thunder. A complex sentence is made up of an independent clause and a dependent clause. The dependent clause in a complex sentence usually begins with a subordinating conjunction or relative pronoun. Subordinating conjunctions include after, although, as, because, before, if, since, unless, until, when, and while. Relative pronouns include that, which, who, whom, or whose. If she ever gets the chance, Terri would love to visit the Egyptian pyramids. During his trip to Italy, Tony visited the Trevi Fountain, which is in Rome. A compound-complex sentence is made up of two or more independent clauses and one or more dependent clauses. After Samantha left work, she stopped at the bank, and then she went to the gym. Sometimes a dependent clause in a complex or compound-complex sentence can interrupt an independent clause. Orcas that are kept in captivity often have bent dorsal fins.
question: Which type of sentence is this? Since it takes approximately one thousand years for a used printer cartridge to decompose, recycling these plastic ink dispensers helps the environment.
choice: (A) compound-complex (B) compound (C) complex (D) simple
context: N/A
answer: C
Rationale:
- 0: A clause is a group of words that contains both a subject and a predicate.
- 1: An independent clause is a complete thought that can stand alone as a sentence.
- 2: A dependent clause (or subordinate clause) is not a complete thought and cannot stand alone as a sentence.
- 3: the oranges on our tree are ripe The clause can stand alone.
- 4: It is independent.
- 5: after we pick up Kevin from work The clause cannot stand alone.
- 6: It is dependent.
- 7: A simple sentence is made up of a single independent clause.
- 8: Ben and I spent all day relaxing by the pool.
- 9: Some simple sentences have introductory phrases, but the introductory phrase is part of the predicate.
- 10: In the winter, Ben usually wears his heavy coat.
- 11: Ben usually wears his heavy coat in the winter.
- 12: A compound sentence is made up of two independent clauses joined by a coordinating conjunction such as and, but, or, or so.
- 13: We saw the flash of lightning, and seconds later we heard a rumble of thunder.
- 14: A complex sentence is made up of an independent clause and a dependent clause.
- 15: The dependent clause in a complex sentence usually begins with a subordinating conjunction or relative pronoun.
- 16: Subordinating conjunctions include after, although, as, because, before, if, since, unless, until, when, and while.
- 17: Relative pronouns include that, which, who, whom, or whose.
- 18: If she ever gets the chance, Terri would love to visit the Egyptian pyramids.
- 19: During his trip to Italy, Tony visited the Trevi Fountain, which is in Rome.
- 20: A compound-complex sentence is made up of two or more independent clauses and one or more dependent clauses.
- 21: After Samantha left work, she stopped at the bank, and then she went to the gym.
- 22: Sometimes a dependent clause in a complex or compound-complex sentence can interrupt an independent clause.
- 23: Orcas that are kept in captivity often have bent dorsal fins.
- 24: The sentence is compound-complex.
- 25: It is made up of two independent clauses and a dependent clause.
- 26: The dependent clause begins with the subordinating conjunction since.
- 27: Since it takes approximately one thousand years for a used printer cartridge to decompose, recycling these plastic ink dispensers helps the environment.
- 28: The answer is A.
generated_skill: The missing skill in this situation is the ability to identify and analyze the structure of complex sentences. The user incorrectly identified the sentence as being a compound-complex sentence, when it is actually a complex sentence.
solution: The sentence is complex. It is made up of an independent clause and a dependent clause. The dependent clause begins with the subordinating conjunction since. Since it takes approximately one thousand years for a used printer cartridge to decompose, recycling these plastic ink dispensers helps the environment.
skill: Is the sentence simple, compound, complex, or compound-complex?
wrong_step_idx: 24
id: 5357
lecture: A fossil is the preserved evidence of an ancient organism. Some fossils are formed from body parts such as bones or shells. Other fossils, such as footprints or burrows, are formed from traces of an organism's activities. Fossils are typically found in sedimentary rocks. Sedimentary rocks usually form in layers. Over time, new layers are added on top of old layers in a series called a rock sequence. The layers in an undisturbed rock sequence are in the same order as when they formed. So, the deeper layers are older than the shallower layers. The relative ages of fossils can be determined from their positions in an undisturbed rock sequence. Older fossils are usually in deeper layers, and younger fossils are usually in shallower layers.
question: Which of the following fossils is younger? Select the more likely answer.
choice: (A) dinosaur footprint (B) insect
context: This diagram shows fossils in an undisturbed sedimentary rock sequence.

answer: B
Rationale:
- 0: A fossil is the preserved evidence of an ancient organism.
- 1: Some fossils are formed from body parts such as bones or shells.
- 2: Other fossils, such as footprints or burrows, are formed from traces of an organism's activities.
- 3: Fossils are typically found in sedimentary rocks.
- 4: Sedimentary rocks usually form in layers.
- 5: Over time, new layers are added on top of old layers in a series called a rock sequence.
- 6: The layers in an undisturbed rock sequence are in the same order as when they formed.
- 7: So, the deeper layers are older than the shallower layers.
- 8: The relative ages of fossils can be determined from their positions in an undisturbed rock sequence.
- 9: Older fossils are usually in deeper layers, and younger fossils are usually in shallower layers.
- 10: Look again at the fossils in the rock sequence diagram.
- 11: Compare the positions of these fossils to determine which one is younger: The dinosaur footprint fossil is in a shallower layer in the rock sequence than the insect fossil.
- 12: So, the dinosaur footprint fossil is most likely younger than the insect fossil.
- 13: The answer is A.
generated_skill: The missing skill in this case is understanding the principle of superposition in geology, which states that in an undisturbed rock sequence, the deeper layers are older than the shallower layers.
solution: Look again at the fossils in the rock sequence diagram. Compare the positions of these fossils to determine which one is younger: The insect fossil is in a shallower layer in the rock sequence than the dinosaur footprint fossil. So, the insect fossil is most likely younger than the dinosaur footprint fossil.
skill: Compare ages of fossils in a rock sequence
wrong_step_idx: 11